Delve into some of the unique benefits of electrical ground support equipment and discover the challenges associated with adopting eGSE.
In a recently published article from Ground Support Worldwide, Mario Pierobon investigates the advantages of eGSE in the aviation industry and highlights the sustainability improvements and operational efficiencies of eGSE over traditional equipment.
The article provides valuable insights from key industry stakeholders including ITW GSE’s Steven Ng, Sales Director Asia Pacific.
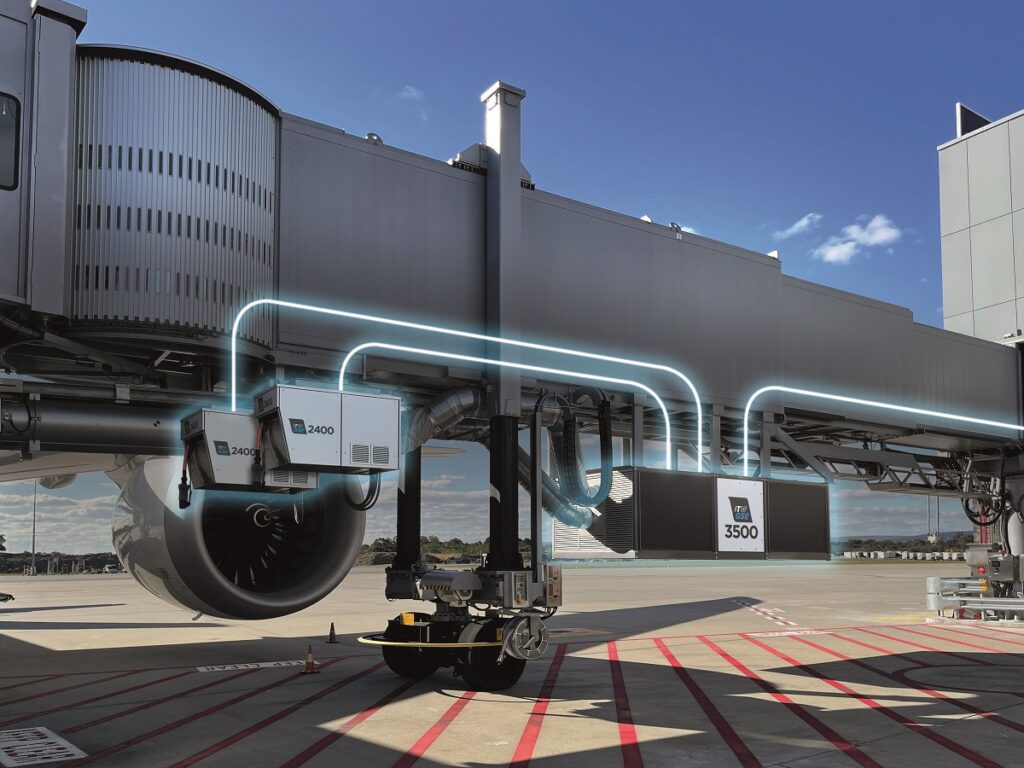
eGPUs are part of the solution
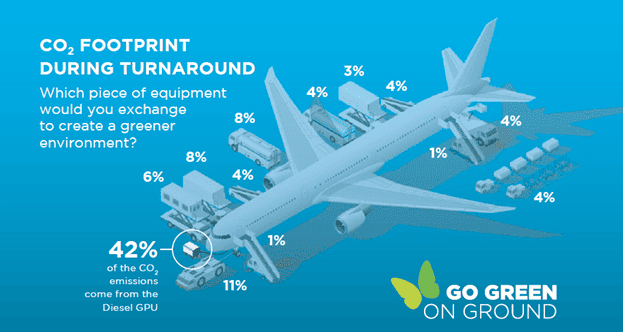
GPUs are responsible for 42% of the CO2 emission during turnarounds, so it’s no wonder that airports are turning to eGPUs to reduce their carbon footprint.
Steven Ng, ITW GSE Sales Director Asia Pacific elaborates on the advantages of eGPUs:
“An eGPU is a zero-emission alternative that uses battery power instead of conventional diesel, meaning it is practically clean, extremely low noise and highly efficient. Customers often highlight the near-silence, the environmental friendliness and the low total cost of ownership, as major advantages of the eGPU,” he says. “When one puts the power on the aircraft, the ground crew can talk to each other even when they are near the eGPU. This also improves ground safety because the communication between the ground crew is clear.”
To learn more about their capabilities and broader applications, read more about eGPU.
Infrastructure challenges
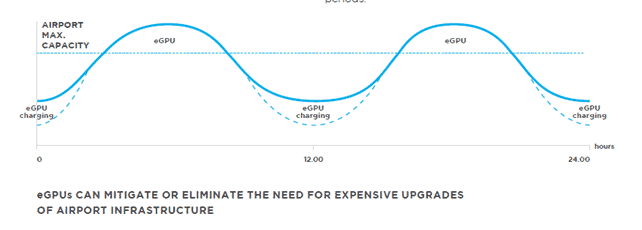
One of the challenges that airports experience is reaching peak load periods with a consumption level close to the maximum power grid capacity of the airport.
Steven Ng explains:
“Increasing the grid capacity requires huge investments in infrastructure and it is very disruptive to operational airports. Having eGPUs as part of the airport’s electrical infrastructure allows one to smooth out the capacity demands over a 24-hour period by charging the eGPUs during periods of low power demand and contribute to a higher utilization rate of the existing grid capacity in the airport.”
Also, there are currently no universal standards in eGSE chargers, meaning that different eGSE may require different charger types. This may potentially pose some challenges to airports trying to implement eGSE.
“Another common challenge is that some airports may find themselves lacking eGSE chargers, largely due to the limitation of existing grid capacity. However, most electric GPUs installed in the airports have excess electrical capacity at the input as most aircraft do not draw full load from the GPU on average,” says Steven Ng.
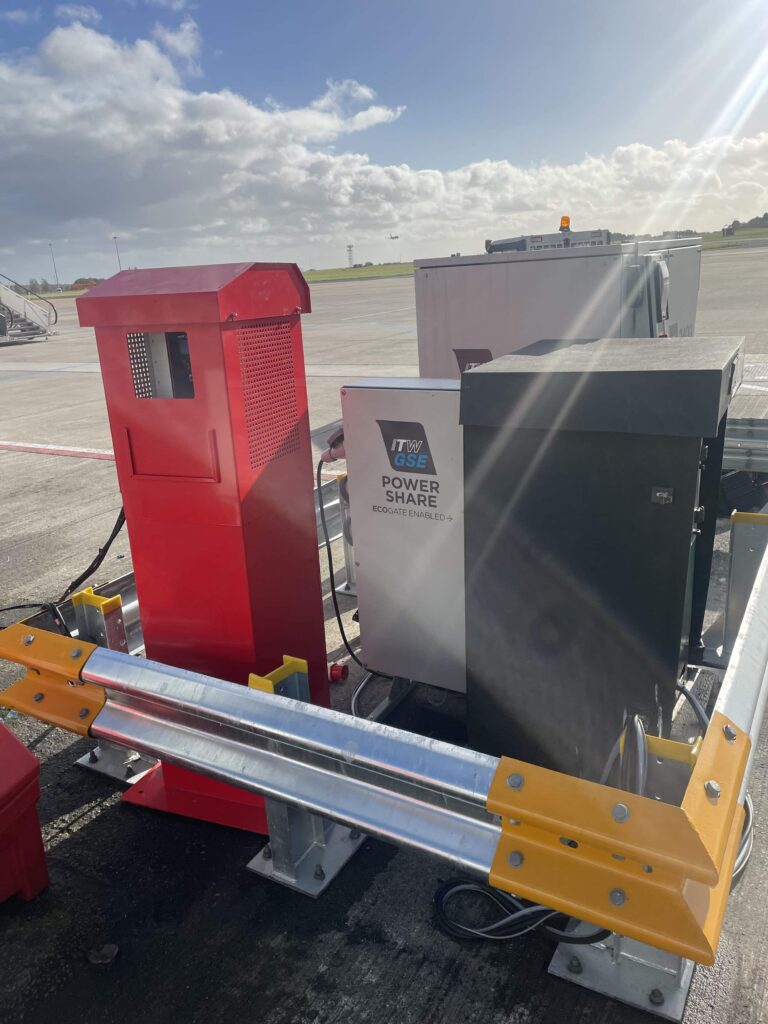
“We have recently introduced a new product to exploit this excess grid capacity. The ITW GSE Power Share technology ensures that the power from the grid to the electric GPUs can be shared and utilised efficiently for other applications, such as to power up a 50/60Hz AC-powered equipment, or charge the eGSE.”
Today’s airports want to modernize and enhance their gate capabilities but may find their options limited by existing electrical infrastructure, affirms Ng.
“Airports are interested in upgrading their existing gate equipment, but often face constraints due to limited power capacity and high costs associated with upgrading their current electrical infrastructure,” he says. “The typical electric GPUs and PCAs, are designed to handle peak loads conditions, which results in around 35-50 percent excess capacity on average. The ITW GSE EcoGate solution can effectively use this surplus capacity to power additional equipment or upgrade existing equipment, without the need to upgrade the existing electrical infrastructure. This technology prioritizes the power demand from the GPUs and ensures that the total power consumption does not exceed a predetermined limit at the gate. This allows improved utilization of the existing grid capacity in the airport without affecting the performance of the gate equipment.”
Read the full article ‚The Unique Benefits of eGSE‚ by Mario Pierobon on Ground Support Worldwide.